Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Overview
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique used to enhance the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) by augmenting the prompt with external, (domain-specific) information retrieved before sending the prompt for inference. This allows models to reason over information they were not originally trained on, making it ideal for enterprise scenarios with private or constantly evolving data.
Why RAG?
LLMs are trained on large corpus of data but are inherently static and limited by their training data and cutoff date. RAG bridges this gap by injecting relevant content from trusted sources into the prompt, increasing reliability and accuracy without retraining the model.
Benefits of RAG:
-
Reduces hallucinations
-
Keeps answers up to date
-
Improves answer precision using curated data
-
Maintains a smaller context window by injecting only relevant information
Core Principles
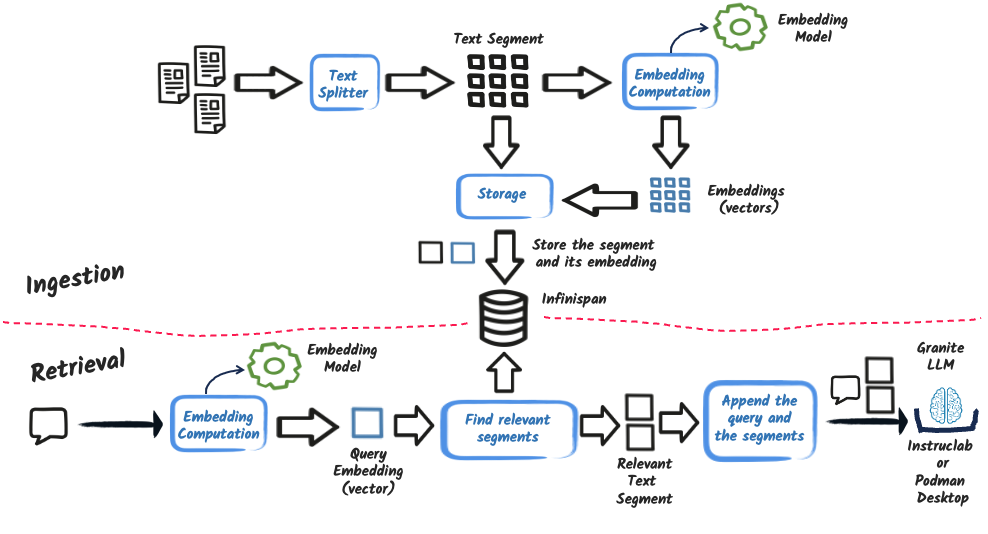
At a high level, a RAG system follows this two-phase process:
-
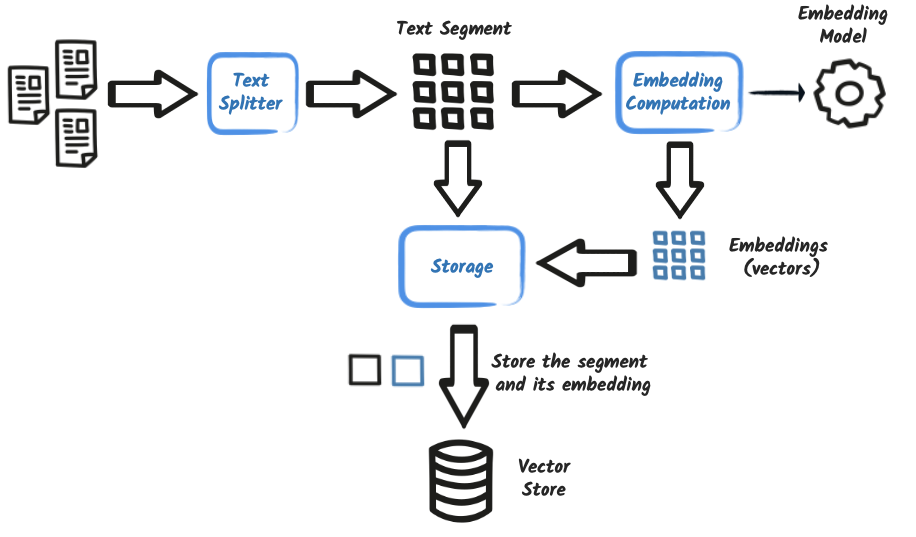
Ingestion: Documents are ingested, segmented (chunked), embedded into vectors, and stored in a vector store.
-
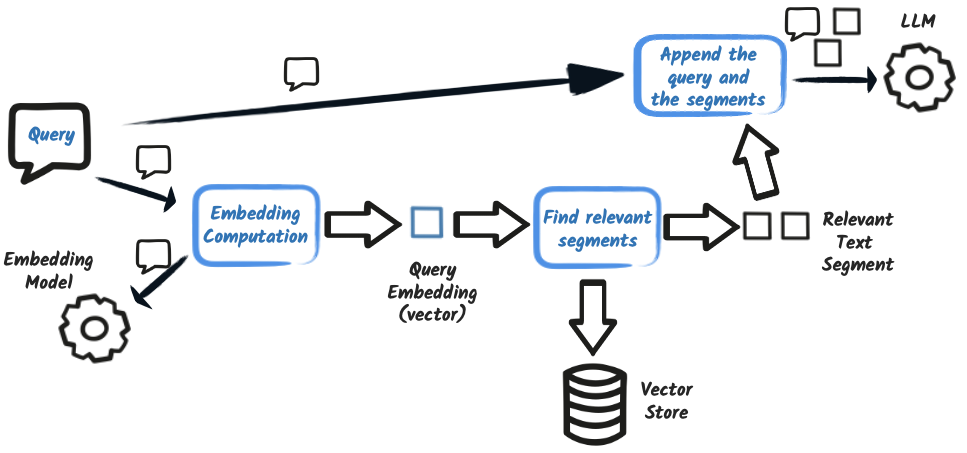
Retrieval: At query time, the question is embedded, relevant segments are retrieved via similarity search, and then sent to the LLM along with the query.
Key Concepts
These concepts are foundational to any RAG-based application:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
Text Splitter |
Divides documents into smaller overlapping or non-overlapping segments for processing. |
Embedding |
A dense vector representation of a text segment computed by an embedding model. |
Embedding Model |
A model trained to convert text into embeddings preserving semantic meaning. |
Vector Store |
A database that allows similarity search over embeddings (e.g., PGVector, Chroma, Weaviate). |
Query Embedding |
The embedding computed from the user’s question. |
Retriever |
A component responsible for finding relevant segments given a query embedding. |
Augmentor |
Optional logic used to enhance the retrieved content (e.g., filtering, re-ranking, transformation). |
Prompt Injection |
Final step of merging query and retrieved content into a prompt for the model. |