Model Context Protocol (MCP) Integration
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that enables seamless integration between AI applications and external data sources, tools, and services. MCP allows LLMs to dynamically discover and execute tools provided by external servers, making it possible to extend AI capabilities without hardcoding integrations.
Quarkus LangChain4j provides comprehensive MCP client support, enabling your AI services to interact with any MCP-compliant server. This integration allows you to:
-
Dynamically discover tools from MCP servers at runtime
-
Execute operations on external systems through standardized protocols (function calling)
-
Access resources like files, databases, or APIs through MCP servers
-
Integrate with the MCP ecosystem, including servers from the official MCP Registry
|
This MCP client implements the specification MCP Specification v2025-11-25. Make sure your MCP servers are compatible with this version of the specification for optimal interoperability. |
|
When to use MCP:
|
Additional Resources
-
General MCP information: modelcontextprotocol.io
-
LangChain4j MCP documentation: MCP in LangChain4j
-
Sample project (STDIO):
mcp-toolssample -
Sample project (Streamable HTTP):
mcp-client-serversample -
MCP Registry: registry.modelcontextprotocol.io
|
Quarkus also provides a dedicated extension for building MCP servers. If you want to create your own MCP server, see: |
Quick Start
Here’s a minimal example to get started with MCP in Quarkus:
1. Add the required dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkiverse.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-langchain4j-openai</artifactId> <!-- or your preferred LLM provider -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkiverse.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-langchain4j-mcp</artifactId>
</dependency>2. Configure your LLM and MCP server:
# Configure your LLM (this example uses OpenAI)
quarkus.langchain4j.openai.api-key=sk-...
# Configure the filesystem MCP server (requires npm installed)
# 'filesystem' is the client name we'll reference later
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.filesystem.transport-type=stdio
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.filesystem.command=npm,exec,@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem,/path/to/allowed/directory3. Create an AI service that uses MCP tools:
import dev.langchain4j.service.SystemMessage;
import dev.langchain4j.service.UserMessage;
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.RegisterAiService;
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp.runtime.McpToolBox;
@RegisterAiService
public interface FileAssistant {
@SystemMessage("""
You are a helpful assistant that can interact with the filesystem.
Help users read, write, and manage files in the allowed directory.
""")
@McpToolBox("filesystem") // Enable tools from the "filesystem" MCP server
String chat(@UserMessage String message);
}4. Use your AI service:
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
import jakarta.ws.rs.GET;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Path;
import jakarta.ws.rs.QueryParam;
@Path("/assistant")
public class AssistantResource {
@Inject
FileAssistant assistant;
@GET
public String chat(@QueryParam("message") String message) {
return assistant.chat(message);
}
}That’s it! Your AI service can now use filesystem operations provided by the MCP server. When a user asks "What files are in the directory?" or "Create a file called notes.txt with the content 'Hello World'", the LLM will automatically use the appropriate MCP tools to fulfill the request.
|
To learn more about AI Services and their features (system messages, memory, streaming, etc.), see the AI Services documentation. |
Dev UI - Testing MCP Clients
When running your application in development mode (mvn quarkus:dev), Quarkus provides a Dev UI interface for exploring and testing your MCP clients.
Access the Dev UI by navigating to http://localhost:8080/q/dev-ui and clicking on the MCP clients card:
The MCP Dev UI provides a comprehensive interface for interacting with your MCP clients:
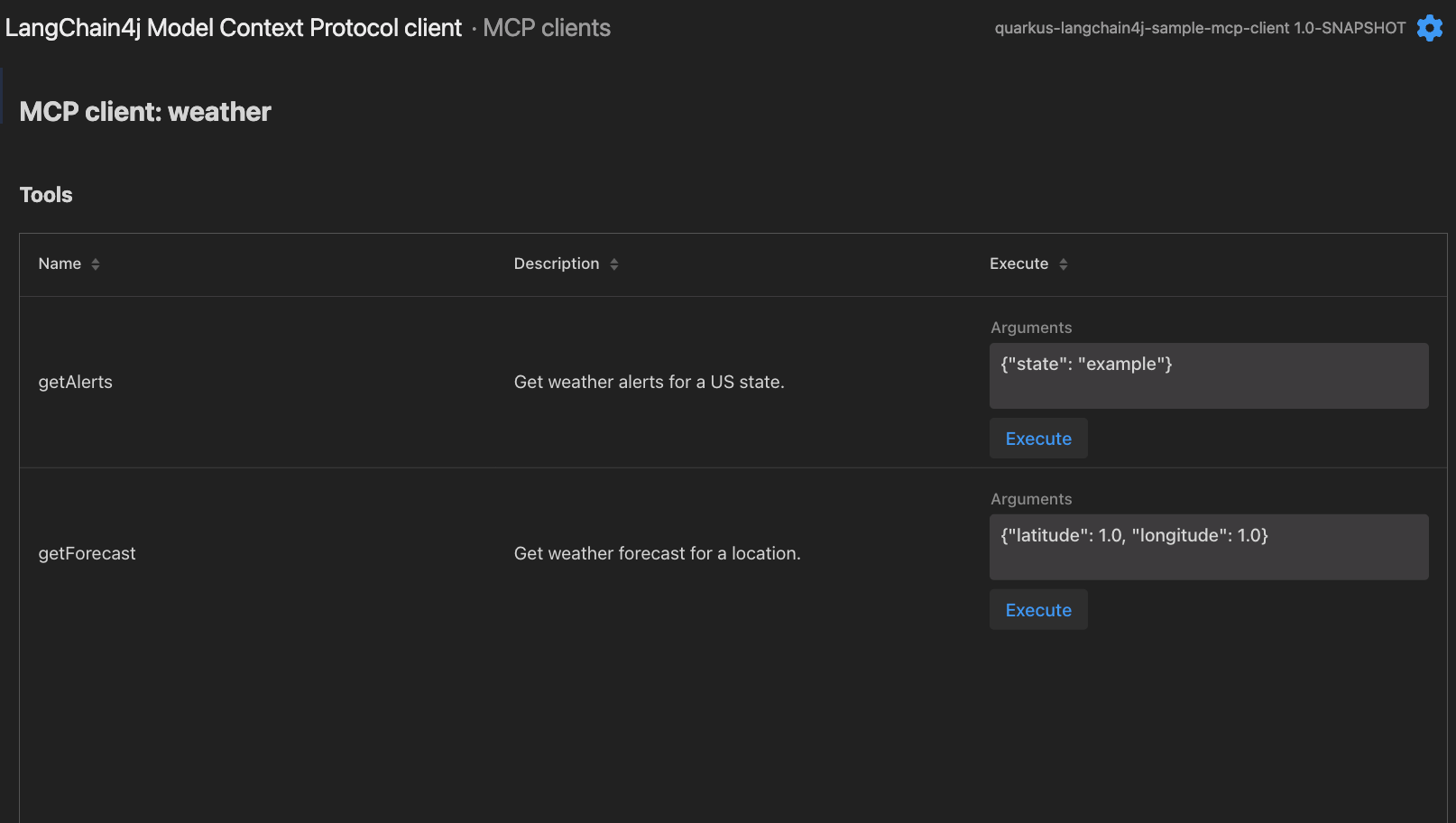
Features:
-
View all configured MCP clients by name
-
Browse all tools available from each MCP client, including:
-
Tool names
-
Tool descriptions
-
Parameter schemas with example values
-
-
Execute MCP tools directly from the UI
-
Pre-populated example inputs based on the tool’s JSON schema
-
Editable argument fields (modify the JSON to test different inputs)
-
Execute button to run the tool
-
Output display showing the tool execution results
-
|
The Dev UI is particularly useful for:
This interactive approach speeds up development by letting you experiment with MCP tools before writing any code. |
Transport Types
MCP supports multiple transport mechanisms for communication between clients and servers. Quarkus LangChain4j supports all standard MCP transports:
STDIO Transport
The STDIO transport spawns an MCP server as a subprocess and communicates through standard input/output streams. This is the most common transport for local MCP servers, especially those distributed as npm packages.
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.transport-type=stdio
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.command=npm,exec,@modelcontextprotocol/server-github
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.environment.GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<YOUR_TOKEN>
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.environment.GITHUB_API_URL=https://api.github.com|
The You can pass environment variables to the subprocess using the |
HTTP Transports
HTTP-based transports connect to remote MCP servers via HTTP. Quarkus supports both streamable HTTP and the SSE (legacy) HTTP transports:
Streamable HTTP (Recommended):
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.remote-server.transport-type=streamable-http
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.remote-server.url=https://mcp-server.example.com/mcpHTTP/SSE (Legacy):
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.remote-server.transport-type=http
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.remote-server.url=https://mcp-server.example.com/mcp/sseWebSocket Transport
This transport is not part of the official MCP specification but is supported by some MCP servers (like those built with quarkus-mcp-server).
The WebSocket transport enables bidirectional communication with MCP servers over WebSocket connections:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.ws-server.transport-type=websocket
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.ws-server.url=ws://localhost:8080/mcpDeclarative Tool Provider Generation
Quarkus automatically generates an MCP-backed ToolProvider from your configuration.
This provider aggregates tools from all configured MCP servers and makes them available to your AI services.
Basic Configuration
Configure one or more MCP servers using named configuration:
# Configure a GitHub MCP server
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.transport-type=stdio
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.command=npm,exec,@modelcontextprotocol/server-github
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.environment.GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<YOUR_TOKEN>
# Configure a filesystem MCP server
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.filesystem.transport-type=stdio
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.filesystem.command=npm,exec,@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem,/home/user/documentsEach configuration block creates an MCP client with the specified name (github, filesystem, etc.).
Using MCP Tools in AI Services
By default, AI services do not automatically use MCP tools.
You must explicitly enable them using the @McpToolBox annotation.
Once enabled, the AI service can discover and execute tools from the specified MCP servers.
Use specific MCP servers:
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp.runtime.McpToolBox;
@RegisterAiService
public interface Assistant {
@McpToolBox("github") // Only use tools from the "github" server
String helpWithGitHub(@UserMessage String message);
@McpToolBox({"github", "filesystem"}) // Use tools from multiple servers
String workWithGitHubAndFiles(@UserMessage String message);
}Use all available MCP servers:
@McpToolBox // No arguments = use all configured MCP servers
String useAllMcpTools(@UserMessage String userMessage);|
The |
Claude Desktop Configuration File
If you’re already using Claude Desktop and have MCP servers configured in its configuration file, you can reuse that configuration in your Quarkus application.
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.config-file=/path/to/claude_desktop_config.jsonThis feature only supports STDIO transport MCP servers. The configuration file is read at build time, so the set of MCP servers is determined when you build your application. However, runtime configuration properties (like environment variables) can still be overridden:
# Use Claude Desktop config file
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.config-file=${user.home}/.config/claude/config.json
# Override environment variable at runtime
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.environment.GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=${GITHUB_TOKEN}MCP Registry Client
The MCP Registry is a centralized repository of community-contributed MCP servers. Quarkus provides a client to discover and query servers from the registry.
| This feature is experimental and may change in future releases. |
Configuration
Configure an MCP registry client:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.registry-client.official.base-url=https://registry.modelcontextprotocol.ioUsing the Registry Client
Inject the registry client into your code:
import dev.langchain4j.mcp.registryclient.McpRegistryClient;
import dev.langchain4j.mcp.registryclient.model.McpServerListRequest;
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp.runtime.McpRegistryClientName;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
@ApplicationScoped
public class McpServerDiscovery {
@Inject
@McpRegistryClientName("official")
McpRegistryClient registryClient;
public void discoverServers() {
// Search for servers
var result = registryClient.listServers(
McpServerListRequest.builder()
.search("filesystem")
.limit(10L)
.build()
);
// Get specific server version
var server = registryClient.getSpecificServerVersion(
"io.github.bytedance/mcp-server-filesystem",
"latest"
);
System.out.println("Found server: " + server.getServer().getDescription());
}
}The registry client supports:
-
Find servers by keywords (search)
-
Get specific versions or all versions of a server
-
Verify registry availability
-
View server descriptions, repositories, packages, and transport information
Exposing MCP Resources as Tools
Some MCP servers provide resources (files, database records, API responses, etc.) that can be accessed programmatically. Quarkus can automatically expose these resources as callable tools, making them directly available to your AI services.
# Enable resources-as-tools feature
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.expose-resources-as-tools=true
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.transport-type=http
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.url=https://mcp-server.example.com/mcp/sseWhen enabled, two synthetic tools are automatically created:
-
list_resources: Lists all available resources from the MCP server -
get_resource: Retrieves the content of a specific resource by URI
Your AI service can then use these tools to discover and access resources:
@RegisterAiService
public interface DataAssistant {
@McpToolBox("myserver")
String analyzeData(@UserMessage String question);
}The AI can now ask questions like "List available resources" or "Show me the content of resource X", and the MCP client will handle the resource retrieval automatically.
Programmatic Access to MCP Clients
While the declarative approach with @McpToolBox is recommended, you can also inject MCP clients directly for programmatic control:
import dev.langchain4j.mcp.client.McpClient;
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp.runtime.McpClientName;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
@ApplicationScoped
public class McpService {
@Inject
@McpClientName("github")
McpClient githubClient;
public void executeTool() {
// List available tools
var tools = githubClient.listTools();
// Execute a tool
var request = /* build tool execution request using ToolExecutionRequest.builder()... */;
var result = githubClient.executeTool(request);
// List resources
var resources = githubClient.listResources();
// Read a specific resource
var content = githubClient.readResource("resource://path/to/resource");
}
}This approach is useful when you need:
-
Fine-grained control over tool execution
-
Custom tool filtering or mapping logic
-
Integration with non-AI parts of your application
-
Programmatic resource access
Providing HTTP headers
For HTTP-based MCP clients, you can inject custom headers into requests sent to the MCP server. There are two ways to do this:
Static headers via configuration properties:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.CLIENT_NAME.header.X-Custom-Header=MyValue
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.CLIENT_NAME.header.X-Another-Header=AnotherValueDynamically provided headers via a McpHeadersSupplier bean:
This is useful when headers need to be generated at runtime dynamically and the supplier needs to be aware of the context of a particular MCP call.
| This is currently supported only with the Streamable HTTP transport. |
Provide a CDI bean that implements the dev.langchain4j.mcp.client.McpHeadersSupplier interface:
import dev.langchain4j.mcp.client.McpCallContext;
import dev.langchain4j.mcp.client.McpHeadersSupplier;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import java.util.Map;
@ApplicationScoped
public class MyHeaderProvider implements McpHeadersSupplier {
@Override
public Map<String,String> apply(McpCallContext context) {
// return a map with headers here
}}When such bean exists, all Streamable HTTP-based MCP clients will be wired up to it automatically.
Authorization
If your MCP server uses the Streamable HTTP or HTTP/SSE transport, it may require client authorization using bearer tokens or API keys.
To support this, implement the McpClientAuthProvider interface to inject credentials dynamically:
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp.auth.McpClientAuthProvider;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
@ApplicationScoped
public class MyMcpAuthProvider implements McpClientAuthProvider {
@Override
public String getAuthorization(Input input) {
String token = retrieveToken(input);
return "Bearer " + token;
}
private String retrieveToken(Input input) {
// Logic to extract token from DB, session, etc.
}
}
The Input object gives you access to the HTTP request context (URI, method, headers).
|
If you have multiple MCP clients, you may need to control which client uses which McpClientAuthProvider.
For that, you can apply the @McpClientName qualifier on beans that implement McpClientAuthProvider, and
that provider will only be used for the specified MCP client (or clients, if you repeat the annotation multiple times).
When resolving which client will use which auth provider, these rules are followed:
- If there is a provider with the matching @McpClientName, it will be used. If there are multiple, it’s not defined which one will be used.
- Otherwise, if there is a provider without @McpClientName, it will be used.
- If neither of the above is true, no authorization will be applied.
Propagating OIDC Access Tokens
If your application uses OpenID Connect (OIDC) and the user has authenticated, you can automatically propagate the user’s access token to the MCP server by adding:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkiverse.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-langchain4j-oidc-mcp-auth-provider</artifactId>
</dependency>This allows the MCP client to act on behalf of the authenticated user (e.g., when calling GitHub APIs).
Logging and Monitoring
Request/Response Logging
Enable detailed logging of MCP client interactions:
# Log all MCP requests and responses
quarkus.langchain4j.log-requests=true
quarkus.langchain4j.log-responses=true
# Or configure per-client
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.log-requests=true
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.log-responses=true
# Enable debug logging for MCP-related classes
quarkus.log.category."dev.langchain4j.mcp".level=DEBUG
quarkus.log.category."io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp".level=DEBUGObserving MCP Log Messages
MCP servers can send log messages to clients. Quarkus automatically:
-
Logs these messages via your application logger
-
Fires CDI events for each log message, enabling custom handling
React to log messages from specific MCP servers:
import dev.langchain4j.mcp.client.logging.McpLogMessage;
import io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp.runtime.McpClientName;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
import jakarta.enterprise.event.Observes;
@ApplicationScoped
public class McpLogObserver {
public void onGitHubLog(@Observes @McpClientName("github") McpLogMessage logMessage) {
System.out.println("GitHub MCP: [" + logMessage.level() + "] " + logMessage.data());
// Custom handling: store in database, trigger alerts, etc.
}
public void onAnyMcpLog(@Observes McpLogMessage logMessage) {
// Observe logs from all MCP clients (no @McpClientName qualifier)
System.out.println("MCP Log: [" + logMessage.level() + "] " + logMessage.data());
// Custom handling: store in database, trigger alerts, etc.
}
}The McpLogMessage includes:
-
data(): The log message as aJsonNode -
level(): Log level asMcpLogLevelenum (DEBUG, INFO, NOTICE, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL, ALERT, EMERGENCY) -
logger(): Logger name from the MCP server
Health Checks
Quarkus automatically registers a readiness health check for all configured MCP clients when the quarkus-smallrye-health extension is present:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-smallrye-health</artifactId>
</dependency>The health check verifies that all MCP servers are responsive by sending an MCP protocol ping message and waiting for a pong response. This works for all transport types (STDIO, HTTP, WebSocket).
For HTTP-based MCP servers, you can optionally use a MicroProfile Health endpoint instead (see below).
Access the health status at /q/health/ready:
{
"status": "UP",
"checks": [
{
"name": "MCP clients health check",
"status": "UP",
"data": {
"github": "OK",
"filesystem": "OK"
}
}
]
}If any MCP client is unhealthy, the overall status becomes DOWN and the data shows the error:
{
"status": "DOWN",
"checks": [
{
"name": "MCP clients health check",
"status": "DOWN",
"data": {
"github": "OK",
"filesystem": "Connection refused"
}
}
]
}MicroProfile Health Integration
For HTTP-based MCP servers only, you can optionally use the server’s MicroProfile Health endpoint instead of the default MCP ping/pong health check.
This is useful when the MCP server is built with quarkus-mcp-server or other frameworks that expose a separate health endpoint.
# Only works for HTTP/Streamable HTTP transports
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.transport-type=streamable-http
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.url=https://mcp-server.example.com/mcp
# Enable MicroProfile health check for this MCP client
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.microprofile-health-check=true
# Customize the health endpoint path (defaults to /q/health)
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.microprofile-health-check-path=/q/healthWhen enabled, the health check:
-
Attempts to call the MicroProfile health endpoint at the configured path
-
Falls back to the standard MCP ping/pong health check if the endpoint returns 404
-
Uses the overall server health status from the endpoint
|
This option is only available for HTTP-based transports. STDIO and WebSocket transports always use the standard MCP ping/pong mechanism. The MicroProfile health endpoint URL is constructed by extracting the base URL (scheme, host, port) from the MCP server URL and appending the configured health path.
For example, if your MCP URL is |
Disabling Health Checks
To disable MCP health checks entirely:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.health.enabled=falseConfiguring Health Check Timeouts
The ping-timeout configuration controls how long to wait for a pong response from the MCP server during health checks. This applies to all transport types:
# Configure ping timeout for health checks (default: 10s)
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.ping-timeout=5s
# Different timeouts for different clients
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.filesystem.ping-timeout=3s
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.remote-server.ping-timeout=15sIf the MCP server doesn’t respond with a pong within the configured timeout, the health check will fail and the overall health status will be DOWN.
Advanced Configuration
Timeouts
Configure various timeout settings for MCP operations:
# Global timeout (applies to all operations unless overridden)
quarkus.langchain4j.timeout=60s
# Tool execution timeout (per MCP client)
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.tool-execution-timeout=30s
# Resource operation timeout (listing and reading resources)
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.resources-timeout=60s
# Ping timeout for health checks
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.ping-timeout=10s
# For MCP Registry clients
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.registry-client.official.read-timeout=10s
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.registry-client.official.connect-timeout=10sTool List Caching
By default, MCP clients cache the tool list and update it when the server notifies of changes:
# Disable caching (always fetch fresh tool list from server)
# Useful for servers that don't support change notifications
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.cache-tool-list=falseMCP Roots
MCP roots define the filesystem boundaries where an MCP server can operate. Similar to workspace folders in IDEs like VSCode, roots specify which directories and files the server has access to. This provides security and access control by restricting server operations to designated locations.
Some MCP servers require a list of workspace roots to function properly. You can configure initial roots in your application properties:
# Provide initial roots (can be updated programmatically at runtime)
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.roots=workspace1=/path/to/workspace1,workspace2=/path/to/workspace2|
Roots are particularly useful for:
The root list can be updated programmatically at runtime using the |
TLS Configuration
For HTTP-based MCP clients, you can specify custom TLS configuration:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.secure-server.tls-configuration-name=my-tls-config
# Configure TLS in Quarkus TLS registry
quarkus.tls.my-tls-config.trust-store.pem.certs=server-ca.pem
quarkus.tls.my-tls-config.key-store.pem.0.cert=client-cert.pem
quarkus.tls.my-tls-config.key-store.pem.0.key=client-key.pemThis is also supported for MCP Registry clients:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.registry-client.official.tls-configuration-name=my-tls-configTroubleshooting
MCP Server Not Starting
Problem: STDIO MCP server fails to start with "command not found" or similar errors.
Solutions:
-
Verify the command path is correct and the executable is available:
which npm npm exec @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem --version -
Use absolute paths for commands:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.filesystem.command=/usr/local/bin/npm,exec,@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem,/path/to/dir -
Check environment variables are correctly passed:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.environment.PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin
Tools Not Available
Problem: @McpToolBox doesn’t provide any tools to the AI service.
Solutions:
-
Verify the MCP client name in
@McpToolBoxmatches your configuration property. For example, if you have:quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.command=...Then use:
@McpToolBox("github") // Must match the name in the configuration String chat(@UserMessage String message); -
Check if automatic tool provider generation is enabled (it should be by default):
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.generate-tool-provider=true -
Enable debug logging to see tool discovery:
quarkus.log.category."io.quarkiverse.langchain4j.mcp".level=DEBUG quarkus.langchain4j.log-requests=true quarkus.langchain4j.log-responses=true -
Verify the MCP server is healthy by checking
/q/healthor/q/health/readyendpoints (Quarkus SmallRye Health extension required and enabled)
Connection Timeouts
Problem: Operations timeout when calling MCP server tools.
Solutions:
-
Increase relevant timeout settings:
quarkus.langchain4j.timeout=120s quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.tool-execution-timeout=120s -
For HTTP servers, check network connectivity and server responsiveness
-
Monitor MCP server logs for performance issues
Authorization Failures
Problem: HTTP MCP server returns 401/403 errors.
Solutions:
-
Implement
McpClientAuthProvideras described in the Authorization section -
Verify credentials are correctly configured:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.github.environment.GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=${GITHUB_TOKEN} -
For OIDC propagation, ensure the user is authenticated and the OIDC extension is configured
-
Enable request logging to inspect authorization headers:
quarkus.langchain4j.mcp.myserver.log-requests=true
Tool Execution Errors
Problem: AI receives errors when executing MCP tools.
Solutions:
-
Check MCP server logs for error details (observe
McpLogMessageevents) -
Verify tool arguments match the expected schema:
quarkus.log.category."dev.langchain4j.mcp".level=DEBUG -
Test the tool directly using programmatic MCP client access to isolate the issue
-
For resource-related tools, verify resources are accessible by the MCP server
Configuration Reference
Configuration property fixed at build time - All other configuration properties are overridable at runtime
Configuration property |
Type |
Default |
|---|---|---|
Whether MCP integration is enabled. If disabled, no MCP clients, registry clients, ToolProvider or MCP health check will be registered. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Whether the MCP extension should automatically generate a ToolProvider that is wired up to all the configured MCP clients. The default is true if at least one MCP client is configured, false otherwise. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
File containing the MCP servers configuration in the Claude Desktop format. This configuration can only be used to configure This file is read at build time which means that which MCP servers the client will use, is determined at build time. However, specific configuration of each MCP server can be overridden at runtime. Environment variable: |
string |
|
Whether the MCP extension should automatically register a health check for configured MCP clients. The default is true if at least one MCP client is configured, false otherwise. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Whether resources should be exposed as MCP tools. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Type |
Default |
|
Whether this MCP client is enabled. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Transport type Environment variable: |
|
|
Whether metrics are published in case a metrics extension is present. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
The URL of the SSE endpoint. This only applies to MCP clients using the HTTP transport. Environment variable: |
string |
|
The command to execute to spawn the MCP server process. This only applies to MCP clients using the STDIO transport. Environment variable: |
list of string |
|
Environment variables for the spawned MCP server process. This only applies to MCP clients using the STDIO transport. Environment variable: |
Map<String,String> |
|
Whether to log requests Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Whether to log responses Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Whether to prefer MicroProfile health checks. Applies to MCP HTTP clients only. If this property is enabled, an HTTP GET call is made to an MCP Server MicroProfile Health endpoint. MicroProfile Health endpoint URL is calculated by extracting a base URL that has no path component from the Default MCP Client health check that opens a Streamable HTTP or SSE transport channel is attempted when a MicroProfile health check returns an HTTP 404 or other error status. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Relative path of an MCP Server MicroProfile Health endpoint. This property is effective only when the MicroProfile Health endpoint URL is calculated by extracting the base URL that has no path component from the Environment variable: |
string |
|
Timeout for tool executions performed by the MCP client Environment variable: |
|
|
Timeout for resource-related operations (retrieving a list of resources as well as the actual contents of resources). Environment variable: |
|
|
Timeout for pinging the MCP server process to check if it’s still alive. If a ping times out, the client’s health check will start failing. Environment variable: |
|
|
The initial list of MCP roots that the client can present to the server. The list can be later updated programmatically during runtime. The list is formatted as key-value pairs separated by commas. For example: workspace1=/path/to/workspace1,workspace2=/path/to/workspace2 Environment variable: |
list of string |
|
The name of the TLS configuration (bucket) used for client authentication in the TLS registry. This does not have any effect when the stdio transport is used. Environment variable: |
string |
|
Static HTTP headers to include in all requests to the MCP server. This only applies to MCP clients using the HTTP or streamable HTTP transport. Environment variable: |
Map<String,String> |
|
Whether to cache the tool list obtained from the MCP server. When set to true (the default), the tool list is cached until the server notifies of changes or the cache is manually evicted. When false, the client always fetches a fresh tool list from the server. This is useful when using MCP servers that don’t support tool list change notifications. Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Type |
Default |
|
The base URL of the MCP registry, without the API version segment. The default value points at the official registry (https://registry.modelcontextprotocol.io). Environment variable: |
string |
|
Whether to log requests Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
Whether to log responses Environment variable: |
boolean |
|
The name of the TLS configuration (bucket) that this MCP client registry will use. Environment variable: |
string |
|
The read timeout for the MCP registry’s underlying http client Environment variable: |
|
|
The connect timeout for the MCP registry’s underlying http client Environment variable: |
|
|
About the Duration format
To write duration values, use the standard You can also use a simplified format, starting with a number:
In other cases, the simplified format is translated to the
|