Diameter Stack Design
Diameter Stack Extensibility
Diameter Stack has been designed to be extensible.
In order to achieve that, two set of APIs are defined by the stack - one that defines basic contracts between the user application and the stack, and one that defines contracts allowing the instance to inject custom objects into the stack to perform certain tasks (for example, SessionFactory). ISessionFactory declares additional methods that allow the developer to declare custom behaviour (for example, custom application sessions).
Please refer to [_jdiameter_source_overview_session_factory] for more detailed information.
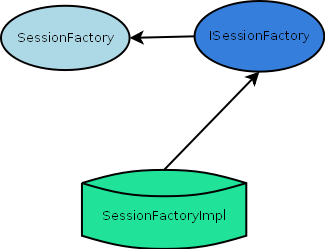
The general pattern for interface declaration is:
-
The interface
ComponentInterfacedeclares the minimal set of methods for a component to perform its task. -
The interface
IComponentInterfaceprovides additional behavior methods. Please refer to the java doc for a list of interfaces and descriptions of method contracts.
Diameter Stack Model
Diameter Stack performs the following tasks:
-
Manages connections to remote peers.
-
Manages session objects.
-
Routes messages on behalf of sessions.
-
Receives and delivers messages to assigned listeners (usually a session object).
Sessions use the stack and the services it provides to communicate with remote peers. The application is the only place that holds references to sessions. It can be seen as follows:
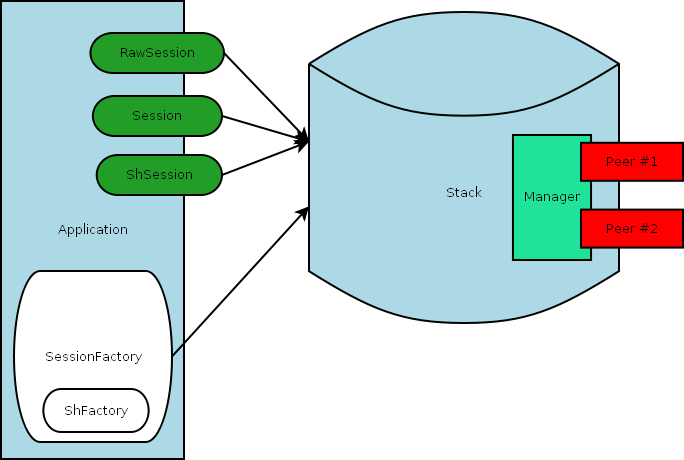
Application Session Factories
Application session factories perform two tasks:
-
server stack as factory for sessions.
-
server session objects as holders for session related resources, like state change listener, event listeners and context.
The figure below shows the relationship between Application Session Factories and User Applications:
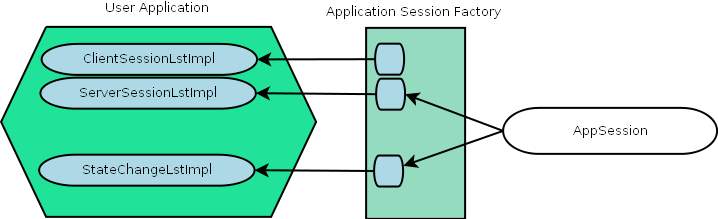
| Session context is a callback interface defined by some sessions. |
Session Replication
Diameter Stack supports replication of session data and state. Clustered stack instances can perform operations on session regardless of physical location. Imagine the logically clustered stack as follows:
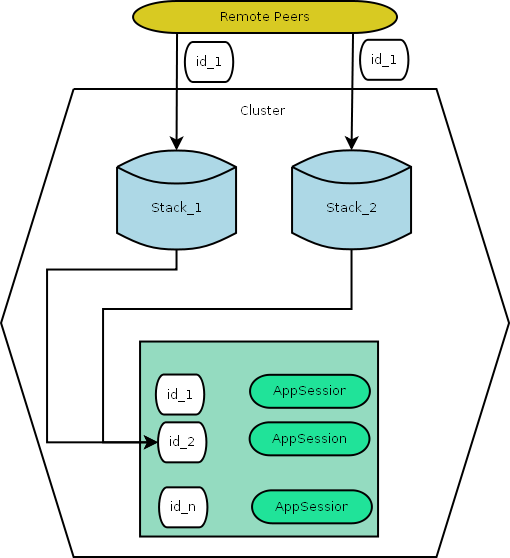
Stack only replicates non simple sessions. This is because simple sessions do not hold state and can be simply recreated by the application. Simple sessions include:
-
RawSessions
-
Sessions
Diameter Cluster replicates the full state of sessions. However, it does not replicate resources that are entirely local to the stack instance, like session listeners. Local resource references are recreated once the session is being prepared to be used in the stack instance. Listeners (state and events) are fetched from the respective session factory instance. See Application Session Factories for more details.